Sharing Our Passion for Technology
& Continuous Learning
TLM Vision
Source Allies partners with companies who want to adopt a long-term, strategic, methodology that aligns technology, services, and the management of the IT infrastructure to business objectives. Implementing a TLM process, beginning with a baseline of the current technology stack / Enterprise Architecture, leads to intentional cost savings and risk reduction as well as having a clean tech stack to grow your skillsets in a focused, valuable way.
Overview
Technology Lifecycle Management (TLM) is a multi-phased approach that encompasses the planning, acquisition, deployment, management, and retirement of all the elements comprising the IT infrastructure. The convergence of in-depth technical knowledge, astute business processes, expert engineering and financial services into a solid business model enables companies to proactively address systematic budgeting and long-term management of their IT infrastructure as well as building proactive skills in the areas needed.
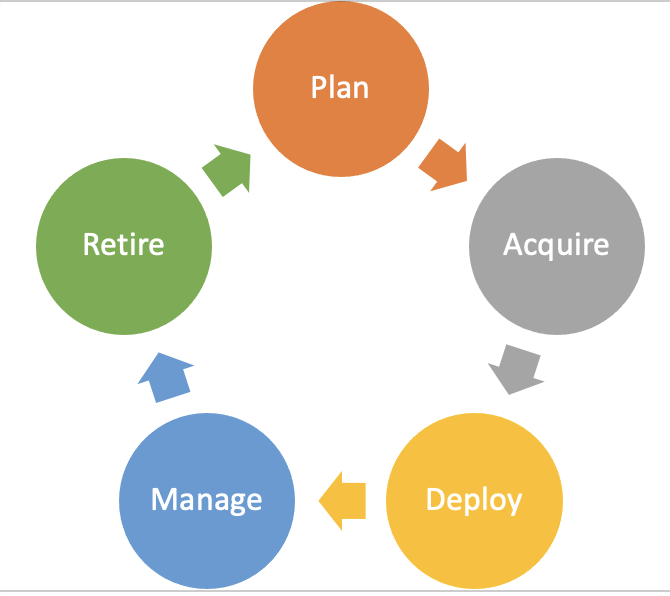
Plan
This phase defines the "what" and "why" and sets the foundation and baseline for all activities going forward. Plan is normally led by a representative of the Business who has a relationship role across the units. Making sure you are meeting the needs of the business, leveraging current infrastructure, and identifying where there are gaps is key. This step also includes evaluating alternative solutions so you do not find yourself purchasing things that do not integrate into the existing solutions or selecting the deal of the day that does not meet the needs of the business. So much waste occurs in the industry when business units purchase solutions that could have been met with the existing technology that they were not aware of. Another inefficiency that occurs by not following these best practices is when there is no plan for the proper personnel (skills and time), how to manage the new items (upgrades and support) and no data retention / end of life plan (security and cost). Many companies find themselves with a surplus of old technology they are supporting with no way to know cost of ownership vs value or a plan on how to streamline the tech stack and architecture.
The key elements of this phase include:
- Business Initiatives, Objectives and Needs Analysis (Why we are considering this)
- Technical Environment Evaluation (Do we already have it?)
- Maintenance overhead projection -- personnel / resources
- Infrastructure capacity / adds?
- Technology Selection and Acquisition Strategy (What are our options?)
- Establish Knowledge Management wiki
- Technology Validation and Refresh Cycles (Would we consider replacing something?)
- Project Planning and Deployment Scheduling
- IT Asset Disposal Strategy -- both what we bring in and what we are removing
- Financial Planning
- Data retention policy
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
- Communication Plan
Acquire
This phase defines the "how" and is normally led by a representative of the financial / contract aspect of the business. The elements of this phase determine the full cost of ownership when bringing in something new. This also defines the scope of what is expected to be done to establish a comprehensive, approved cost.
The key elements of this phase include:
- Finalization of financing
- Project planning
- Acquisition and Commissioning tool
- Acquisition infrastructure
- Personnel / resource additions needed
- Training materials for experts, users and support personnel
- Enhance Knowledge Management wiki
- Communication
Deploy
This phase defines the "who" and "when" and should be led by an Enterprise Architect / Technical environment knowledge leader. This phase coordinates and executes all the elements of deployment as listed below. This person is closely assisted by a member of the project management organization.
The key elements of this phase include:
- System configuration and image loading, with design verification and quality assurance
- IT Asset management
- Certified project manager who maintains the scope definition, mitigates risks, collaborates with end users, uses resources efficiently, and adheres to the budget.
- IT security
- Well-planned implementation of a data repository / migration
- Engineers with certifications specific to the underlying technology must implement all IT infrastructure components
- Enhance Knowledge Management Wiki
- Service Desk training
- End user training
- Monitoring configured
- Communication
Manage
This phase begins after deployment and is coordinated by the IT Service Management and Engineering / Infrastructure knowledge resources. The ongoing health, value and other key elements as listed below are critical to the long-term success of meeting the original needs as defined in the Plan phase. It is critical that the representatives at this phase clearly understand the intended purpose, SLA and value expected.
The key elements of this phase include:
- Configuration and change management, technology restoration, and software upgrades
- Maintenance agreements and warranties
- Proactive incident monitoring, technical phone and onsite support, and parts replacement
- Monitoring capabilities that include the ability to accurately manage the state of the IT asset and its support history
- On-going collaboration between our company and the vendor
- Periodic reviews to discuss performance metrics
- Evaluate / upgrade the IT infrastructure to keep up with increasing user demands
- Enhance Knowledge Management Wiki
- General Communications
- Reporting
- Security
- Archival of data -- data retention policy
- Track usage and collect feedback
Retire
This phase is coordinated by the IT Service Management representative. They are closely assisted by the Engineering / Infrastructure representative for the execution of the elements listed below. The resources executing this phase should be referencing the decisions that were made in the Plan phase and making updates to those original ideas as needed.
The key elements of this phase include:
- Disposing and Reconditioning
- Monitor usage and communicate to end users
- End of life / repurpose IT assets: Assess the true cost of repurposed technology such as security risks, patches and replacement parts, and out-of-warranty repairs
- Data security
- Update Knowledge Management wiki for historical reference
Getting started - Key team roles and language update
This first iteration / adoption includes all roles meeting to update any verbiage / language needed to establish how to adopt this best practice into the culture. Establishing templates and putting the process into your Agile / PM tool as a template for all future projects will empower a single source of knowledge and a place to continuously improve.
The kickoff of all TLM projects would include establishing the following roles.
- Business Process knowledge (initiatives, objectives, needs analysis - Plan phase)
- Financial/Contract knowledge (Acquire Phase)
- Technical knowledge (Environment - Deploy phase)
- Expert engineering knowledge (Integration, Asset disposal - Manage phase)
- ITSM (Data retention, SLA - Manage and Retire phase)
- Project Management (PM, scheduling, communication - Overarching coordination)





